Erectile function is an essential aspect of male sexual health, often taken for granted until it becomes a problem.
Understanding how erections work is the first step in addressing any challenges, including erectile dysfunction (ED). In this comprehensive article, we explore the physiology and psychology behind erections and ED. We'll also discuss how solutions like the VaxAid hydropump can help combat these challenges.
How Erections Work
The Role of Blood Flow
Erections are largely a vascular event, involving a complex coordination between neurological, vascular, and psychological elements. When a man is sexually aroused, signals from the brain activate a chain of chemical events that lead to the dilation of blood vessels in the penis. This causes blood to flow into the corpora cavernosa, two sponge-like chambers running the length of the penis. The influx of blood causes the penis to expand and become rigid, resulting in an erection.
Hormones and Neurotransmitters
Hormones like testosterone and neurotransmitters such as nitric oxide play a crucial role in regulating this process. Nitric oxide acts as a signaling molecule that prompts the dilation of blood vessels, facilitating the inflow of blood.
Why Erections Sometimes Don't Work: Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Physiological Factors
- Vascular Issues: Conditions like atherosclerosis can narrow or block arteries, affecting blood flow to the penis.
- Neurological Disorders: Diseases like multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s can interfere with the brain’s ability to send signals needed for an erection.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Low testosterone levels can hinder the erection process.
- Medications: Certain medications can affect blood flow or hormonal balance.
- Physical Injury: Damage to the pelvic area or spinal cord can interfere with the erection process.
Psychological Factors
- Stress: The stress hormone cortisol can inhibit the body's sexual response.
- Anxiety and Depression: Mental health issues can distract the mind, preventing sexual arousal.
- Performance Anxiety: The fear of sexual failure can create a cycle of ED.
- Relationship Issues: Lack of emotional connection with a partner can hinder sexual function.
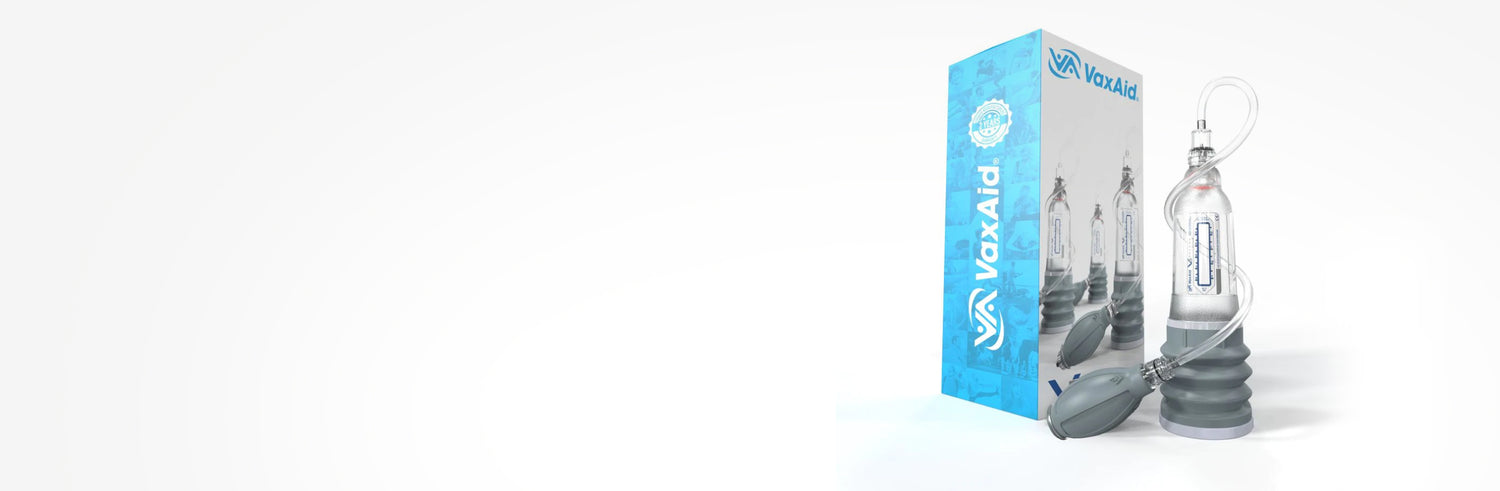
Using VaxAid Hydropump to Combat ED
The VaxAid hydropump is a device designed to assist in achieving and maintaining an erection, and it can address both physiological and psychological factors contributing to ED.
How It Works
The VaxAid hydropump uses water to create a vacuum around the penis. This encourages blood to flow into the corpora cavernosa, mimicking the natural erection process. The use of water provides a uniform force around the penis, making it safer and more effective than air-based pumps.
Physiological Benefits
- Improved Blood Flow: Regular use can help increase vascular health, improving blood flow to the penis.
- Penile Rehabilitation: Post-surgical or post-injury, the hydropump can aid in penile tissue recovery.
- Hormonal Balance: Improved sexual function can contribute to a healthier hormonal balance.
Psychological Benefits
- Confidence Boost: Successful use of the device can improve self-esteem and reduce performance anxiety.
- Enhanced Sexual Pleasure: Improved erection quality can lead to a more satisfying sexual experience, alleviating psychological barriers.
The VaxAid take
Understanding how erections work and the factors contributing to ED is essential for finding effective treatment solutions. The VaxAid hydropump offers a multi-faceted approach to combating ED, addressing both physiological and psychological aspects of erectile function. However, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment options tailored to individual needs.